A nurse is counseling a woman about prenatal vitamins and focuses on the need for folic acid intake. Which disorder is a potential consequence of inadequate folic acid intake?
Down syndrome
Cerebral palsy
Neurofibromatosis
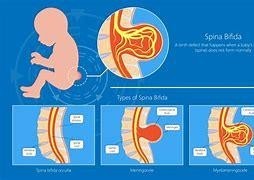
Spina bifida
The Correct Answer is D
Spina bifida is a birth defect that occurs when the neural tube, which forms the brain and spinal cord, does not close properly during early fetal development. This can result in an opening in the spine that exposes the spinal cord and nerves, leading to various complications such as paralysis, bladder and bowel problems, hydrocephalus, and learning difficulties. Folic acid is a B vitamin that is essential for the formation of the neural tube and other organs in the embryo. Inadequate folic acid intake before and during pregnancy can increase the risk of spina bifida and other neural tube defects.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
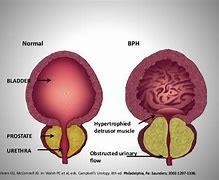
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a noncancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, a walnut-sized organ that surrounds the urethra in men. The enlarged prostate can compress the urethra and cause urinary problems, such as difficulty starting or stopping urination, weak urine stream, frequent or urgent urination, and blood in the urine. Transurethral prostate resection (TURP) is a surgical procedure that removes excess prostate tissue and relieves the pressure on the urethra.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
This condition is an infection of the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves, which can cause vegetation to form on the valve surfaces. Vegetations are masses of microorganisms, inflammatory cells, and fibrin that adhere to the valve leaflets and can interfere with their function. The symptoms of endocarditis may include fatigue, fever, night sweats, chills, weight loss, or heart murmur.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
