How is purified follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) (urofollitropin [Metrodin]) administered to an infertile woman as part of the pharmacologic treatment?
Intranasal spray
Intramuscular injection
Vaginal suppository
Tablet
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason: Intranasal spray is not a correct option, as urofollitropin is not available in this form. Intranasal spray is a method of delivering some medications through the nose, where they can be absorbed by the mucous membranes. However, urofollitropin is a protein hormone that would be degraded by the enzymes in the nasal cavity and would not reach the bloodstream effectively.
Choice B reason: Intramuscular injection is the correct option, as urofollitropin is available in this form. Intramuscular injection is a method of delivering medications into the muscle tissue, where they can be absorbed by the blood vessels. Urofollitropin is a protein hormone that needs to be injected into the body to bypass the digestive system and avoid being broken down by the stomach acids and enzymes. Urofollitropin is usually injected into the thigh or buttock muscles once a day for several days, depending on the dosage and the response².
Choice C reason: Vaginal suppository is not a correct option, as urofollitropin is not available in this form. Vaginal suppository is a method of delivering medications into the vagina, where they can be absorbed by the vaginal walls or act locally. Urofollitropin is a protein hormone that would not be absorbed well by the vaginal mucosa and would not reach the ovaries, where it is supposed to stimulate the development of the follicles (eggs).
Choice D reason: Tablet is not a correct option, as urofollitropin is not available in this form. Tablet is a method of delivering medications orally, where they can be swallowed and absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract. Urofollitropin is a protein hormone that would be destroyed by the stomach acids and enzymes and would not reach the bloodstream or the ovaries.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason: Infection is not the greatest risk for a woman with marginal placenta previa, as it is not directly related to the condition. Marginal placenta previa is a type of placenta previa where the edge of the placenta is near the cervical os but does not cover it. It can cause painless bleeding during pregnancy or labor, but it does not increase the risk of infection.
Choice B reason: Hemorrhage is the greatest risk for a woman with marginal placenta previa, as it can occur due to the separation of the placenta from the uterine wall during labor or delivery. The bleeding can be profuse and life-threatening, and it requires prompt intervention and monitoring.
Choice C reason: Urinary retention is not the greatest risk for a woman with marginal placenta previa, as it is not directly related to the condition. Urinary retention is the inability to empty the bladder completely, and it can occur due to various factors such as anesthesia, trauma, or medication. It can cause discomfort, infection, or bladder distension, but it is not as serious as hemorrhage.
Choice D reason: Thrombophlebitis is not the greatest risk for a woman with marginal placenta previa, as it is not directly related to the condition. Thrombophlebitis is the inflammation of a vein due to a blood clot, and it can occur due to prolonged bed rest, dehydration, or injury. It can cause pain, swelling, or redness in the affected area, and it can lead to pulmonary embolism if the clot dislodges and travels to the lungs. However, it is not as common or as severe as hemorrhage.
Correct Answer is ["B","C","D"]
Explanation
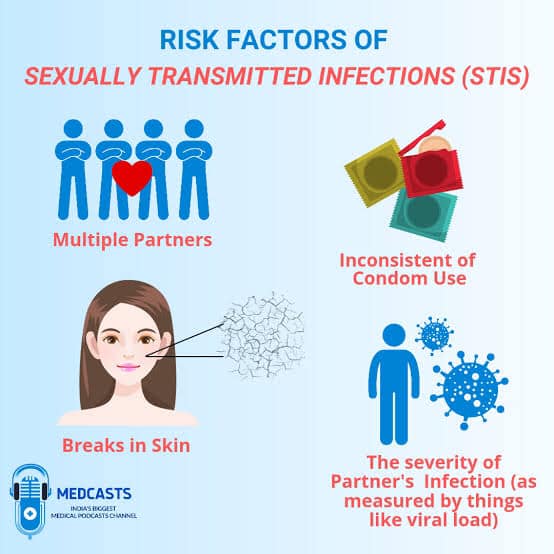
Choice A reason: Abstinence is the avoidance of sexual activity, which reduces the risk of exposure to STIs. It is not a sexual risk behavior.
Choice B reason: Multiple sex partners increases the likelihood of exposure to STIs, especially if the partners are not tested or treated. It is a sexual risk behavior.
Choice C reason: Unprotected anal intercourse exposes the mucous membranes of the rectum and anus to potential pathogens, which can cause STIs such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis, and HIV. It is a sexual risk behavior.
Choice D reason: Oral sex involves contact between the mouth and the genitals or anus, which can transmit STIs such as herpes, HPV, gonorrhea, and syphilis. It is a sexual risk behavior.
Choice E reason: Dry kissing is the contact between the lips without the exchange of saliva, which does not transmit STIs. It is not a sexual risk behavior.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
