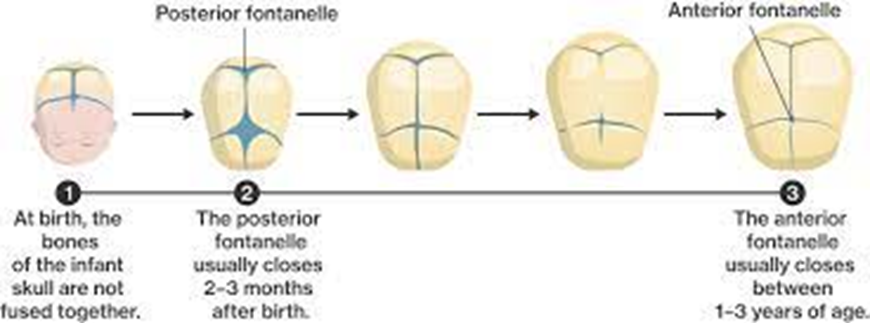
The nurse is doing a routine assessment on a 19-month-old infant and notes that the anterior fontanel is closed. This should be interpreted as:
An abnormal finding-indicates the need for developmental assessment.
A normal finding.
An abnormal finding-indicates the need for immediate referral to a practitioner
A questionable finding-the infant should be rechecked in 1 month.
The Correct Answer is B
A. An abnormal finding-indicates the need for developmental assessment.
This is not accurate. The closure of the anterior fontanel within the expected age range does not indicate an abnormal finding or the need for additional developmental assessment.
B. A normal finding.
This is the correct interpretation. The anterior fontanel normally closes between 12 to 18 months, and closure by 19 months is within the expected developmental range.
C. An abnormal finding-indicates the need for immediate referral to a practitioner.
This is not necessary based on the information provided. The closure of the anterior fontanel within the expected timeframe is a normal finding.
D. A questionable finding-the infant should be rechecked in 1 month.
There's no need for rechecking in 1 month. The closure of the anterior fontanel at 19 months is considered normal.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Ridiculing their fears so they understand that there is no need to be afraid.
This option is not recommended. Ridiculing a child's fears can be emotionally harmful and may lead to increased anxiety. It's important to approach fears with empathy and support.
B. Using logical persuasion to explain away their fears and help them recognize how unrealistic the fears are.
While providing information and reassurance is important, simply dismissing or explaining away a child's fears may not be sufficient. Preschoolers may need more concrete strategies and involvement in managing their fears.
C. Actively involving them in finding practical methods to deal with the frightening experience.
This is the recommended choice. Actively involving preschoolers in finding practical methods allows them to participate in the process, promoting a sense of control and autonomy. It encourages them to develop coping skills.
D. Forcing them to confront the frightening object or experience in the presence of their parents.
Forcing a child to confront their fears may intensify anxiety and is generally not a recommended approach. It's essential to respect a child's pace and provide support as they work through their fears.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Document B/P not obtained because the child was in the playroom.
This is not the best option. The nurse should attempt to obtain the blood pressure as part of routine monitoring.
B. Take the child back to their room, take their B/P and then take them back to the playroom.
This may disrupt the child's play and is not the most efficient approach for routine blood pressure monitoring.
C. Take the child to the treatment room.
This might be unnecessary for a routine blood pressure check and could cause unnecessary anxiety for the child.
D. Take the B/P in the playroom.
This is the best intervention. If possible, taking the blood pressure in the playroom allows the child to remain in a familiar and comfortable environment, reducing anxiety and promoting cooperation.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
