Which of the following describes the action of an agonist?
A molecule that prevents receptor activation by other medications
An endogenous molecule or a medication that can activate a receptor
A medication that increases the affinity of a receptor for a different medication
A therapeutic agent that both blocks and activates a receptor
The Correct Answer is B
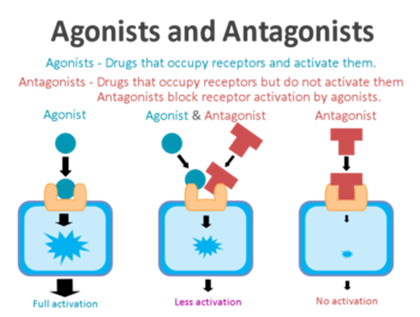
An agonist is a molecule that can bind to and activate a receptor to induce a biological response ³. Agonists can be endogenous molecules, such as hormones or neurotransmitters, or medications that mimic the action of endogenous agonists ³.
Option A is incorrect because an agonist does not prevent receptor activation by other medications.
Option C is incorrect because an agonist does not increase the affinity of a receptor for a different medication.
Option D is incorrect because an agonist does not both block and activate a receptor.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
An accidental administration of a dose greater than recommended can result in toxicity. This means that the medication reaches harmful levels in the body and can cause damage to organs or other adverse effects.
Option A is incorrect because an overdose is more likely to increase side effects rather than decrease them.
Option B is incorrect because a lowered therapeutic threshold means that a lower dose of medication is needed to achieve the desired effect, which is not related to an overdose.
Option D is incorrect because an overdose can increase the effectiveness of the medication to dangerous levels, rather than decrease it.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Donepezil is a medication used to treat Alzheimer's dementia. Its main mechanism of action is the inhibition of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme in the brain ¹. This increases the availability of acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses ⁵, which can improve cognition and function in clients with Alzheimer's dementia ¹.
Option B is incorrect because donepezil does not decrease acetylcholine in the periphery to increase movement.
Option C is incorrect because donepezil does not delay the transmission of acetylcholine at the neuronal junction.
Option D is incorrect because donepezil does not bind dopamine at neuron receptor sites to increase ability.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
