An adolescent client has just been found to have broken one of the unit rules. The nurse imposes the consequence of losing phone privileges. In this instance, the nurse is acting as the:
Parent Surrogate
Caregiver
Advocate
Teacher
The Correct Answer is A
A. Parent Surrogate: A parent surrogate refers to someone who acts as a substitute or stand-in for a parent, making decisions and providing care in the absence of the actual parent. While nurses may provide parental guidance and support, especially in therapeutic settings for adolescents, imposing consequences for rule-breaking is not necessarily acting as a parent surrogate.
B. Caregiver: A caregiver is someone who provides physical and emotional care to individuals in need, such as patients or clients in healthcare settings. While nurses do fulfill the role of caregivers by providing support and meeting the needs of their patients, imposing consequences for rule-breaking is not primarily an aspect of the caregiver role.
C. Advocate: An advocate is someone who speaks up on behalf of another person to ensure their rights, preferences, and well-being are respected and promoted. While nurses do advocate for their patients in various ways, such as advocating for their healthcare needs or treatment preferences, imposing consequences for rule-breaking is not typically considered an advocacy role.
D. Teacher: A teacher is someone who imparts knowledge, skills, and guidance to others, typically in an educational or instructional setting. While nurses may provide education and guidance to their patients, especially regarding health-related topics, imposing consequences for rule-breaking is not directly related to the role of a teacher.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Cognitive therapy:
Cognitive therapy is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and beliefs that contribute to emotional and behavioral issues. While cognitive therapy can be beneficial for addressing cognitive distortions and maladaptive thinking, it is more individual-focused and may not provide the group dynamics and social learning opportunities offered by milieu therapy.
B. Reality therapy:
Reality therapy is a therapeutic approach that emphasizes personal responsibility, choice, and action to address current problems and meet basic needs. While reality therapy focuses on individual accountability and decision-making, it may not specifically target group interactions and social skill development as milieu therapy does.
C. Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT):
Dialectical behavioral therapy is a type of cognitive-behavioral therapy that combines elements of cognitive therapy and mindfulness techniques to help individuals regulate emotions, improve interpersonal skills, and manage distress. While DBT includes group skills training components, its primary focus is on individual therapy sessions and may not provide the same emphasis on group interactions and social learning as milieu therapy.
D. Milieu therapy.
Milieu therapy focuses on creating a therapeutic environment or community where clients can interact and engage in activities that promote positive social behaviors and enhance basic living skills. In milieu therapy, clients participate in group activities, social interactions, and structured routines designed to improve their communication skills, socialization, and daily living skills. The goal of milieu therapy is to create a supportive and structured environment that facilitates learning, socialization, and behavior change within a group setting.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Akathisia: Akathisia is a side effect of antipsychotic medications characterized by restlessness, agitation, and a strong urge to move. It is not typically associated with tongue protrusion, lip smacking, or rapid eye blinking.
B. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: Neuroleptic malignant syndrome is a rare but serious reaction to antipsychotic medications, characterized by fever, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, and autonomic dysfunction. It is not associated with the specific symptoms described in the scenario.
C. Dystonia: Dystonia is a movement disorder characterized by sustained or repetitive muscle contractions, leading to abnormal postures or repetitive movements. It can occur as a side effect of antipsychotic medications but typically presents differently from the symptoms described in the scenario.
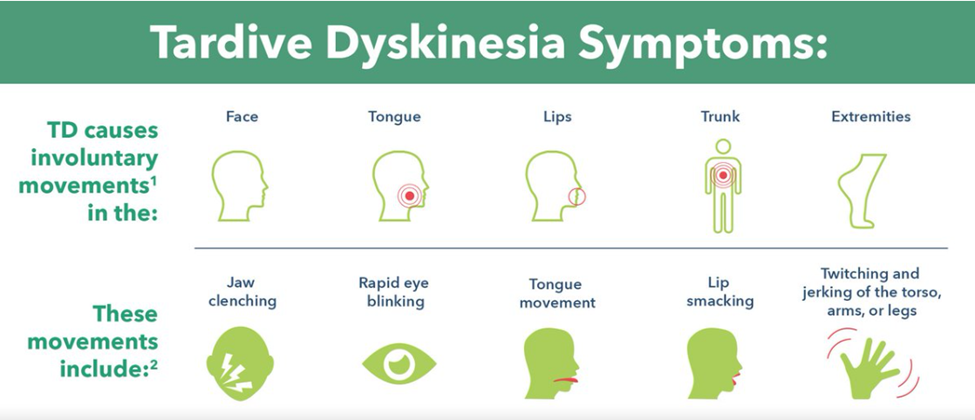
D. Tardive dyskinesia: Tardive dyskinesia is a chronic syndrome characterized by involuntary, repetitive movements of the face, tongue, and other body parts. It is associated with long-term use of conventional, first-generation antipsychotic medications. Symptoms can include tongue protrusion, lip smacking, rapid eye blinking, and other abnormal movements.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
