Miami Dade College Pharmacology NUR1141
Miami Dade College Pharmacology NUR1141
Total Questions : 57
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreA toddler ingests a small amount of household cleaning fluid. What is the safest advice for the nurse to provide the caregiver?
Explanation
A. Give the child fluids and proceed to the emergency department.
While giving the child fluids is generally important, proceeding to the emergency department without consulting poison control may not be the most appropriate initial action. Poison control can provide specific guidance based on the substance ingested.
B. Call the poison control center and follow directions.
The safest advice for a toddler who has ingested a small amount of household cleaning fluid is to call the poison control center and follow their directions. Poison control centers are staffed with professionals who can provide specific guidance based on the type and amount of the ingested substance. They can advise on the appropriate steps to take, such as whether immediate medical attention is needed or if monitoring at home is sufficient.
C. Administer syrup of ipecac and monitor for vomiting.
The use of syrup of ipecac is no longer recommended as a routine measure for ingested substances. It can have adverse effects and may not be effective for all substances. Consulting poison control for guidance is considered a more appropriate approach.
D. Have the toddler eat bread to absorb the substance.
The ingestion of certain substances may not be effectively addressed by having the toddler eat bread. The specific advice for management should come from poison control, which can provide evidence-based guidance.
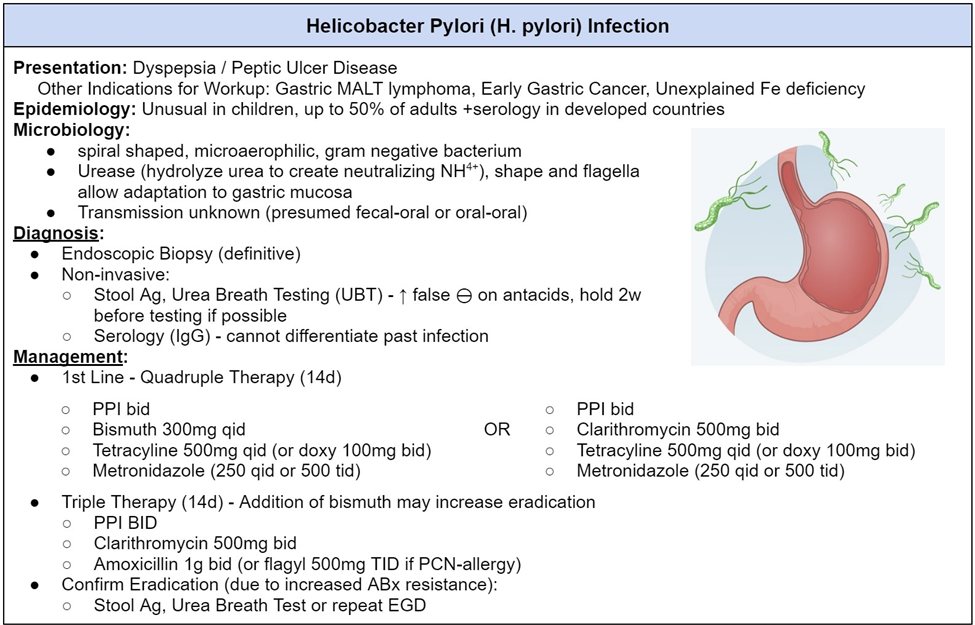
A patient with peptic ulcer disease is noted to have a positive breath test for H. pylori. What will the nurse anticipate the health care provider will order?
Explanation
A. Antacids and narcotics.
Antacids can provide temporary relief of symptoms, but they do not treat the underlying H. pylori infection. Narcotics are not typically used as a standard treatment for peptic ulcer disease related to H. pylori.
B. Pepsin inhibitors and antiemetics.
Pepsin inhibitors and antiemetics may address symptoms but do not target the H. pylori infection directly. The standard treatment involves antibiotics to eradicate the bacteria and proton pump inhibitors to reduce acid production.
C. Proton pump inhibitors and antibiotics.
A positive breath test for H. pylori indicates the presence of Helicobacter pylori bacteria, which is associated with peptic ulcer disease. The standard treatment for H. pylori infection involves a combination of proton pump inhibitors (to reduce stomach acid production) and antibiotics (to eradicate the bacteria).
D. Emetic agents and tranquilizers.
Emetic agents are used to induce vomiting and are not indicated for the treatment of H. pylori infection. Tranquilizers are not part of the standard treatment for peptic ulcer disease associated with H. pylori.

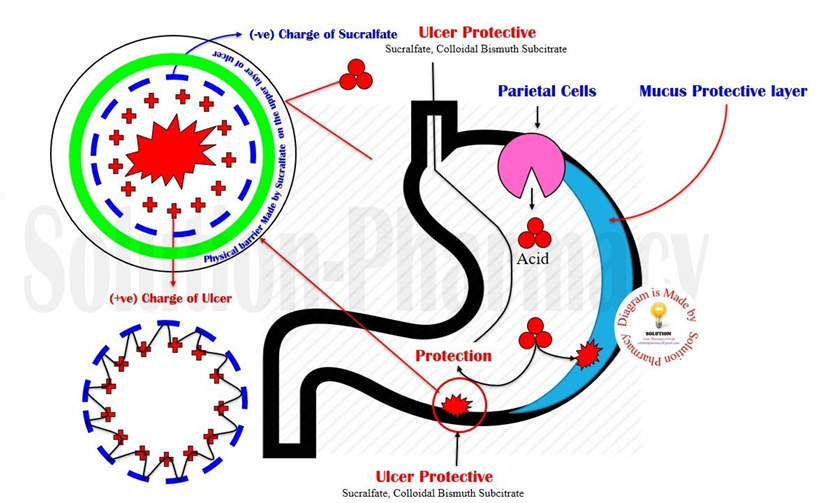
A patient with a gastric ulcer is ordered sucralfate (Carafate). How does this medication works?
Explanation
A. Calm the patient to reduce acid production.
This description is not accurate for sucralfate. Calming the patient to reduce acid production is typically associated with medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 receptor blockers.
B. Block the H2 receptors.
Blocking H2 receptors is the mechanism of action for H2 receptor blockers, such as ranitidine. It is not the mechanism of action for sucralfate.
C. Neutralize the gastric acids.
Neutralizing gastric acids is the mechanism of action for antacids, such as aluminum hydroxide or calcium carbonate. Sucralfate works differently; it forms a protective coating on the gastric lining rather than directly neutralizing acids.
D. Coat the gastric lining.
This is the correct mechanism of action for sucralfate. It forms a protective coating on the gastric lining, adhering to the ulcer site and providing a barrier against gastric acid.
A patient who complains of gastric distress from NSAIDS such as aspirin or indomethacin will most likely benefit from the administration of which medication?
Explanation
A. Misoprostol (Cytotec)
The patient complaining of gastric distress from NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) like aspirin or indomethacin may benefit from the administration of misoprostol (Cytotec). Misoprostol is a prostaglandin analog that helps protect the stomach lining and reduce the risk of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers.
B. Lansoprazole (Prevacid)
Lansoprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that reduces stomach acid production. While PPIs can be used for certain acid-related conditions, they do not directly protect against NSAID-induced gastric distress.
C. Magaldrate (Riopan)
Magaldrate is an antacid that neutralizes stomach acid. It may provide relief from symptoms of indigestion but does not specifically address the gastric distress caused by NSAIDs.
D. Magnesium trisilicate (Gaviscon)
Magnesium trisilicate is an antacid that helps neutralize stomach acid. Like magaldrate, it may alleviate symptoms of indigestion but does not target the underlying issue of NSAID-induced gastric distress.
A patient is suspected to have peptic ulcer disease from H. pylori. The patient asks the nurse what kind of testing will be done to determine the cause of the peptic ulcer. What will the nurse tell the client?
Explanation
A. Blood cultures will need to be drawn.
Blood cultures are not typically used for diagnosing H. pylori infection. Instead, specific blood tests, such as serology or antibody tests, may be employed to detect antibodies against H. pylori.
B. A biopsy of the stomach will be done.
While a biopsy may be taken during an upper endoscopy to examine the stomach lining for ulcers and H. pylori infection, it is not the primary method for detecting the presence of H. pylori. The biopsy may be used for confirming the infection and assessing the severity of damage.
C. A breath test will be performed.
This is the correct choice. The breath test is a common and non-invasive method used to detect the presence of H. pylori. The patient drinks a solution containing a substance that H. pylori can break down, and the detection of carbon dioxide in the patient's breath indicates the presence of the bacteria.
D. Computerized scanning will identify if H. pylori is present.
Computerized scanning, such as computed tomography (CT) scans, is not a primary method for detecting H. pylori. Imaging studies are not typically used for H. pylori diagnosis, and the methods mentioned earlier, like breath tests and endoscopy, are more commonly employed.
A patient is ordered bisacodyl (Dulcolax). Before administering the drug, it is most important for the nurse to assess the patient for what?
Explanation
A. Hypertension
Hypertension is not a specific concern related to the use of bisacodyl. Bisacodyl is a laxative, and high blood pressure is not typically considered a contraindication for its use.
B. Anemia
Anemia is not a specific concern related to the use of bisacodyl. The primary focus before administering bisacodyl is to assess for signs or symptoms of appendicitis, as its use is contraindicated in cases of suspected appendicitis.
C. Allergy to penicillin
Allergy to penicillin is not relevant in the context of administering bisacodyl. These are unrelated medications with different mechanisms of action, and allergy to penicillin does not impact the administration of bisacodyl.
D. Appendicitis
This is the correct choice. Before administering bisacodyl, it is crucial to assess the patient for signs or symptoms of appendicitis. The use of bisacodyl is contraindicated in cases of suspected appendicitis, as it may stimulate bowel activity and worsen the condition.
A patient is ordered a phenothiazine antiemetic for treatment of nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy. The nurse will be evaluating for a positive effect. At what time should the nurse administer the drug?
Explanation
A. As requested by the patient.
Administering the drug only when requested by the patient may not provide adequate prophylaxis against chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. These medications are often prescribed on a schedule to prevent symptoms rather than treating them reactively.
B. 1 hour after chemotherapy administration.
Waiting until 1 hour after chemotherapy administration may not cover the full period during which nausea and vomiting are likely to occur. The administration schedule for antiemetics is often more extended to provide better coverage.
C. The night before the treatment, the day of the treatment, and for 24 hours after the treatment.
This is the correct choice. Administering phenothiazine antiemetics according to this schedule helps ensure continuous coverage during the critical period when chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting are most likely to occur.
D. The day of treatment.
Administering the drug only on the day of treatment may not provide sufficient coverage for the entire duration when chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting can occur. Again, the schedule mentioned in option C is more comprehensive for prevention.
The nurse is instructing a patient who will take psyllium (Metamucil) to treat constipation. What information will the nurse include when teaching the patient?
Explanation
A. The importance of consuming adequate amounts of water
When instructing a patient who will take psyllium (Metamucil) to treat constipation, it is crucial to emphasize the importance of consuming adequate amounts of water. Psyllium is a bulk-forming laxative that works by absorbing water in the intestines, forming a gel-like mass that helps soften stools and promote bowel movements. Without sufficient water intake, psyllium may cause an obstruction or worsen constipation.
B. The need to monitor for systemic side effects.
Psyllium is generally well-tolerated and is not associated with significant systemic side effects. The primary consideration is ensuring proper hydration.
C. The onset of action of 30-60 minutes after administration.
Psyllium is not a fast-acting laxative. It usually takes a longer time to produce its effects, and patients should not expect an immediate response within 30-60 minutes.
D. The need to use the dry form of psyllium to prevent cramping.
Using the dry form of psyllium is not recommended, as it may increase the risk of choking or swallowing difficulties. It is typically recommended to mix psyllium with a sufficient amount of water or other liquids to prevent cramping and ensure proper absorption.
The nurse is deciding on a dosage schedule for methylphenidate (Ritalin). The nurse recognizes that which time is the most appropriate to administer this drug for maximum effectiveness?
Explanation
A. Before breakfast or lunch
Methylphenidate (Ritalin), a stimulant medication commonly used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), is usually administered before breakfast or lunch for maximum effectiveness. This schedule helps align the peak concentration of the medication with the times when increased focus and attention are often needed, such as during school hours.
B. With meals
While it can be administered with meals, the goal is often to have the medication take effect before meals to help with focus and attention during activities like school or work.
C. After dinner
Administering methylphenidate after dinner may interfere with the patient's ability to fall asleep, as the medication can cause insomnia. It is generally recommended to avoid administering it in the late afternoon or evening.
D. At bedtime
Administering methylphenidate at bedtime is not appropriate due to the potential for insomnia. The stimulant effect of the medication is not aligned with the patient's sleep-wake cycle.
How will the parents of a 8 year old child diagnosed with ADHD most typically describe their child's behavior?
Explanation
A. A learning disorder and muscle paralysis
This description does not align with the typical symptoms of ADHD. ADHD is characterized by core symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Muscle paralysis is not a recognized symptom of ADHD.
B. Nervousness and sleeplessness
While some individuals with ADHD may experience difficulties with sleep, nervousness and sleeplessness are not the primary symptoms of ADHD. ADHD is more characterized by difficulties with attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
C. Hyperactivity and decreased attention span
This is the correct choice. Hyperactivity and a decreased attention span are core symptoms of ADHD. Children with ADHD often display impulsive behaviors, have difficulty sustaining attention, and may be overly active.
D. Hyperactivity and nervousness
While hyperactivity is a common symptom of ADHD, nervousness is not typically described as a core symptom. ADHD is more characterized by impulsivity, hyperactivity, and attention difficulties.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 57 questions on the Miami Dade College Pharmacology NUR1141 Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



