A patient arrives at the emergency department with abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. A physical examination reveals acute pain at the McBurney point. A CT scan confirms the diagnosis, and surgery is immediately scheduled to prevent peritonitis. Based on this information, which diagnosis is described?
Inguinal hernia
Gastroenteritis
Cholelithiasis
Acute appendicitis
The Correct Answer is D
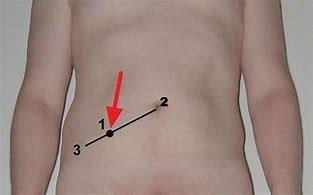
Acute appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch attached to the large intestine that has no known function. It can cause abdominal pain that usually starts around the navel and then shifts to the lower right quadrant, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fever, and constipation or diarrhea. The McBurney point is a spot located about two-thirds of the way from the navel to the right hip bone that is tender when pressed in patients with appendicitis. A CT scan can show signs of inflammation and enlargement of the appendix and rule out other causes of abdominal pain. Surgery (appendectomy) is the standard treatment for appendicitis to remove the inflamed appendix and prevent complications such as peritonitis (infection of the lining of the abdominal cavity) or abscess (collection of pus) formation.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Acute appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch attached to the large intestine that has no known function. It can cause abdominal pain that usually starts around the navel and then shifts to the lower right quadrant, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fever, and constipation or diarrhea. The McBurney point is a spot located about two-thirds of the way from the navel to the right hip bone that is tender when pressed in patients with appendicitis. A CT scan can show signs of inflammation and enlargement of the appendix and rule out other causes of abdominal pain. Surgery (appendectomy) is the standard treatment for appendicitis to remove the inflamed appendix and prevent complications such as peritonitis (infection of the lining of the abdominal cavity) or abscess (collection of pus) formation.

Correct Answer is ["A","B","C"]
Explanation
a. Air bubble in the artery or vein- thromboembolism (air embolism, occurs when air
enters the bloodstream and blocks blood flow to vital organs. It can be caused by
trauma, surgery, injection, or diving)
b. Bulging sac of blood in an artery- aneurysm (it occurs when a weak spot in an artery
wall balloons out and fills with blood. It can be caused by high blood pressure,
atherosclerosis, infection, or genetic factors)
c. Clot of blood in an artery- thrombus (arterial thrombosis, which occurs when a blood
clot forms in an artery and blocks blood flow to tissues or organs. It can be caused by
atherosclerosis, injury, inflammation, or hypercoagulable states)
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
